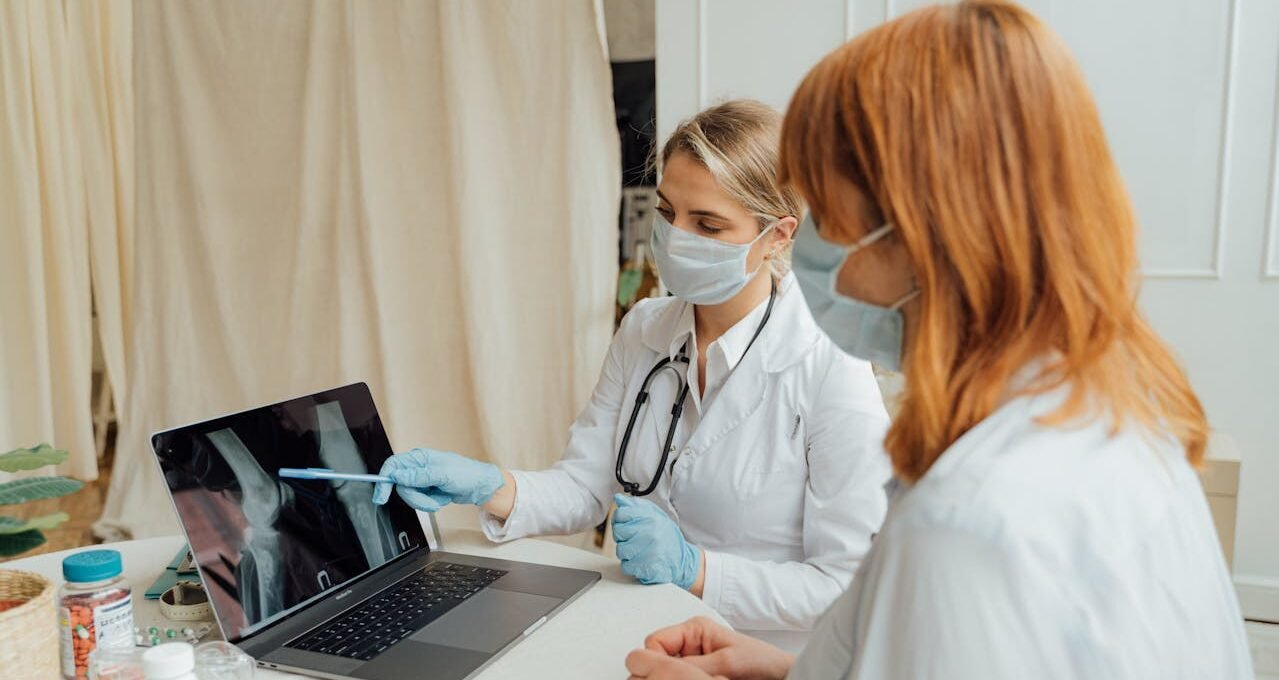
Globally, osteoporosis is a serious health risk for women, especially as they get older. Osteoporosis is a disease indicated by weakened bones that increases the risk of fractures and greatly decreases the quality of life, but preventive measures can preserve bone health and stave off osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis in Women
Weak bone mass and bone tissue breakdown are the main symptoms of osteoporosis, which increases bone weakening and fracture risk. Despite the fact that osteoporosis may disturb people of any gender, women are more vulnerable than men because of things like hormonal fluctuations and decreasing bone density after menopause.
Risk Factors for Osteoporosis
- Age and Gender
The decrease in estrogen levels occurs after menopause, and women over the age of fifty are more likely to develop osteopenia.
- Hormonal Changes
Estrogen has a major role in maintaining bone density. Women have a decline in estrogen during menopause, which increases their susceptibility to osteoporosis and bone loss.
- Family History
If osteopenia or fractures exist in the family, a person may be at great risk of acquiring the condition.
- Lifestyle Factors
Osteopenia can be brought on by bad lifestyle choices, including eating a diet low in calcium and vitamin D, smoking, being sedentary, and binge drinking.
Importance of Preventive Measures
Preventive action plays an essential role in lowering the risk of osteoporosis and maintaining bone health over time. Women can strengthen their bones and lessen the effects of osteopenia by applying certain strategies and adopting healthy lifestyle practices.
1. Dietary Strategies for Preventing Osteoporosis
Keep your bones as healthy as possible by eating a balanced diet high in calcium, magnesium, vitamin D, and vitamin K.
- Calcium-Rich Foods
Include foods high in calcium in your diet habitually, such as almonds, dairy products, and fortified meals with green leaves.
- Vitamin D Sources
Ensure a suitable intake of vitamin D from the sun, fortified foods, meals high in fat, egg yolks, and other sources.
- Magnesium and Vitamin K
Add foods high in magnesium, such as whole grains, seeds, and nuts; also include foods high in vitamin K, like spinach, broccoli, and kale.

2. The Role of Exercise in Osteoporosis Prevention
Regular exercise is necessary to build and maintain strong bones.
- Weight-Bearing Exercises
Take part in weight-bearing activities to increase bone density and encourage bone formation, such as stair climbing, running, dancing, and walking.
- Strength Training
To strengthen the bones and muscles, engage in strength training exercises with free weights, weight machines, or resistance bands.
- Balance and Flexibility Exercises
Rehearsal balance exercises like yoga and Tai Chi expand stability and lessen the risk of drops and fractures.

3. Lifestyle Modifications for Bone Health
- Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol
Excessive binge drinking and smoking can weaken bones and raise the chance of fractures. To stimulate bone health, give up smoking and consume less alcohol.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight
To lessen the load on bones and joints, conserve a healthy weight with a healthy diet and everyday exercise.
- Fall Prevention Strategies
Use fall prevention techniques, including incorporating handrails and grab bars, clearing out threats from the house, and wearing proper footwear.
- Regular Bone Density Screening
Regular bone density examinations are recommended for women, particularly those who are at higher risk, in order to evaluate bone health and identify osteoporosis early.
4. Hormonal Balance and Osteoporosis Prevention
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Talk to your doctor about hormone replacement treatment (HRT) as a way to manage menopausal symptoms and maintain hormonal balance, which lowers the risk of osteopenia.
- Alternative Therapies
To promote hormonal balance and bone health, investigate complementary therapies, including herbal supplements, acupuncture, and chiropractic adjustments.
Conclusion
In order to protect women’s bone health and lower their risk of osteoporosis, preventive actions are crucial. Women may strengthen their bones and preserve lifetime skeletal health by implementing a comprehensive program that includes nutritional choices, exercise lifestyle alternations, frequent tests, and hormonal balance.
FAQs
What age is appropriate for women to begin osteoporosis prevention?
Bone health should be given priority by women from an early age and should be maintained through lifelong prevention, particularly after menopause.
Can lifestyle modifications reverse the effects of osteoporosis?
Although altering one’s lifestyle can stop more bone loss, treating osteoporosis already present may call for taking medication along with lifestyle changes.
Are there any osteoporosis natural therapies available?
Although the effectiveness of some herbs and supplements varies, it is still advisable to visit a healthcare professional since they may promote bone health.
How often should bone density screenings be performed?
Individual risk factors determine how often a person should get a bone density examination. This is something you should discuss with a healthcare professional.
Does osteoporosis just affect women in their later years?
Even though osteoporosis is more frequent in elderly women, younger women can still lower their chance of developing difficulties by taking preventative actions to safeguard their bone health.

